Sulphur 386 Jan-Feb 2020
31 January 2020
Market Outlook
Market Outlook
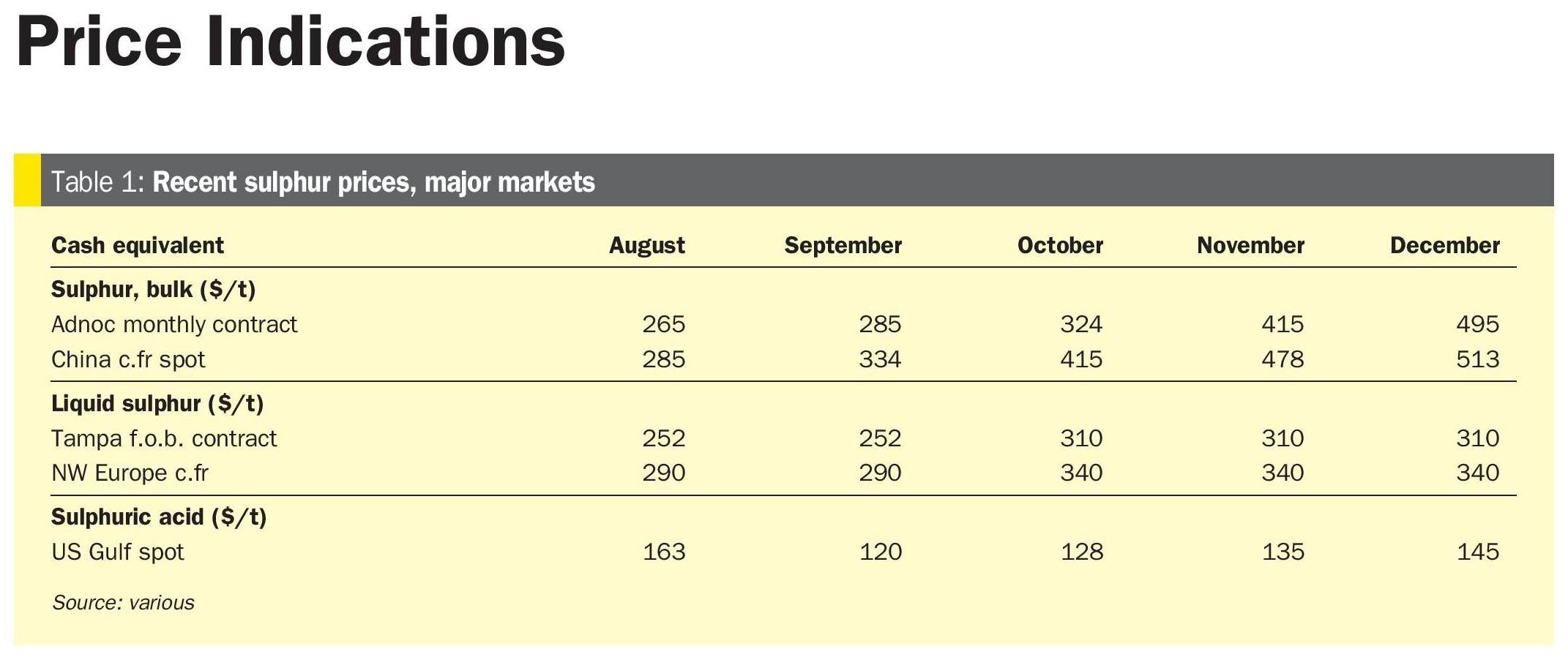
SULPHUR
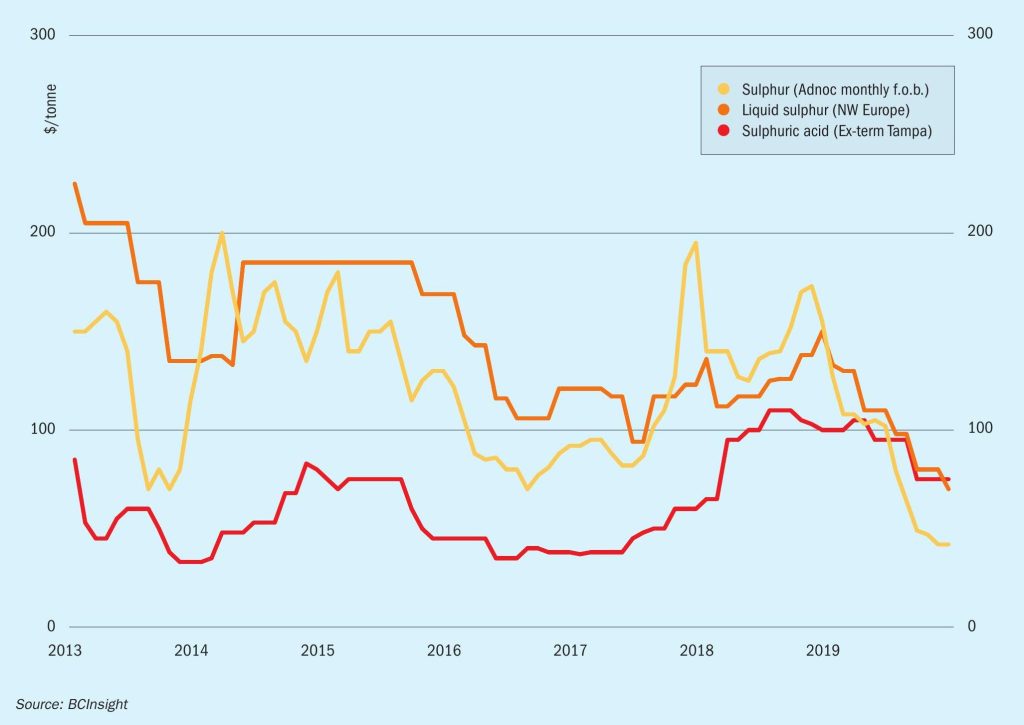
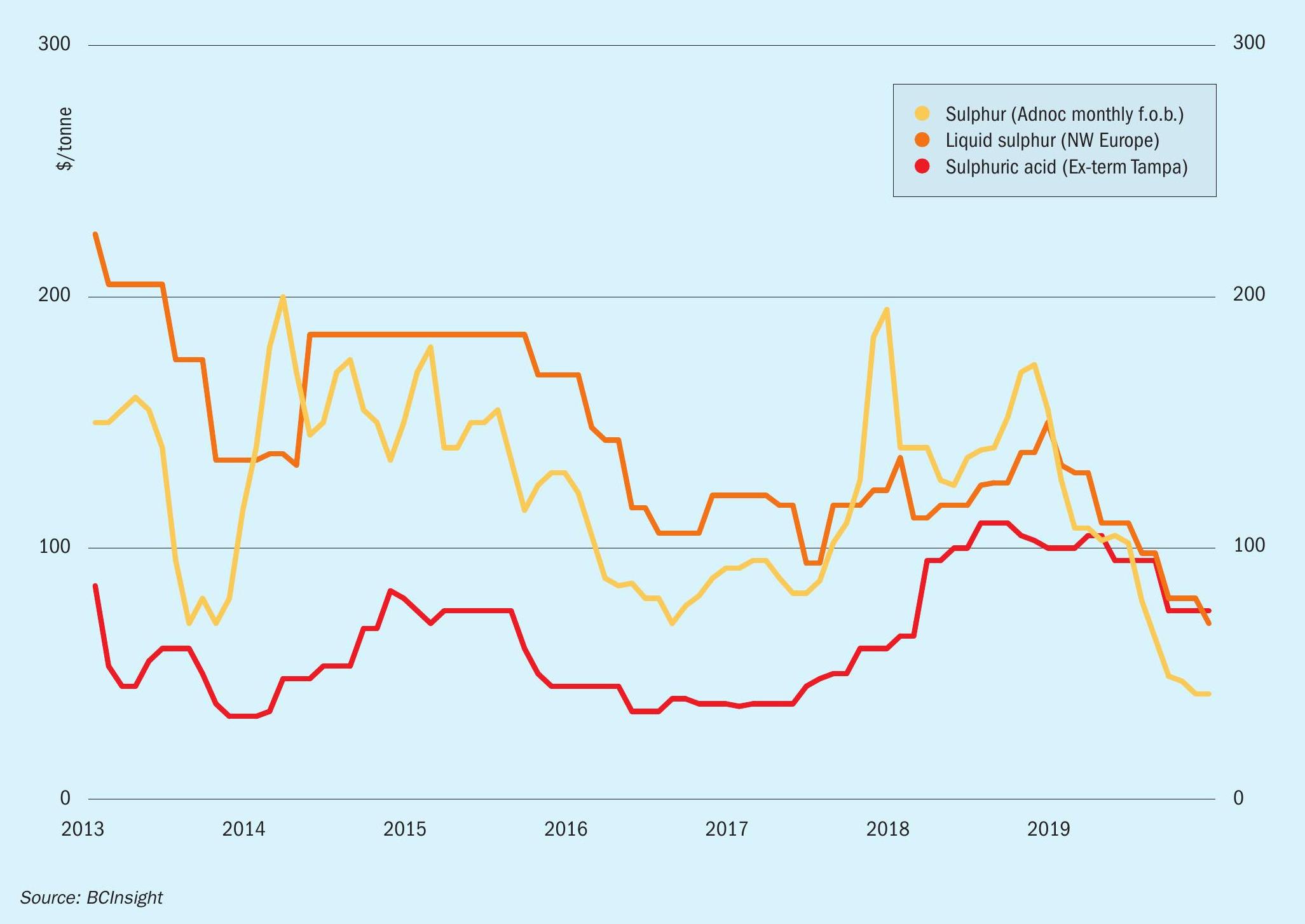
- How the processed phosphates market develops over the coming months will be a major factor for the short term outlook for sulphur trends. Improvement is anticipated in the phosphates market from around mid-2020 which may help to support sulphur demand and in turn pricing.
- China remains a major influencing factor on global pricing and trade for the year ahead. Price recovery will depend on recovery in the domestic fertilizer season in the spring. High sulphur stocks at ports and domestic DAP production cuts alongside the slowdown over the Lunar new year period are bearish factors weighing on the market.
- New export volumes from the Middle East region are expected in 2020 as projects in Qatar and Kuwait come online, adding to the global sulphur balance
- Outlook: Prices are expected to remain stable in the short term with demand fundamentals pointing to any increases in price trends to be short lived. The rollover from Middle East producers for January points to support for stability in the short term. Reduced shipments to North Africa to major buyer OCP is a bearish factor due to the weak phosphates market and high inventories, as is reduced participation of Chinese players in the market for several weeks from mid-January.
SULPHURIC ACID
- The presence of China as a major exporter remains a market bear for the outlook. We expect to see volumes offered to international markets in the medium term period, as surplus availability remains a feature of the local market.
- Prices in SE Asia have been stable to soft in recent months ranging $30-38/t c.fr in mid-January. Spot activity has been limited with many buyers covered through the first quarter of 2020. Year to date imports for Thailand, Indonesia and Malaysia were all down 3-15% year on year.
- Brazil imported 451,000 t acid in 2019, reflecting an 18% decline on a year earlier; weak demand and domestic production margins impacted offtake. Spain remained the leading supplier at 215,000 t, up 24%, while Belgium and Mexico shipped 122,000 t and 60,000 t respectively.
- DRC production of sulphur based acid is set to rise with the start-up of the new KCC burner. This will lead to Zambian smelter acid from the Mopani smelter into other markets.
- Chilean production is forecast to rise slightly in the medium term on the back of improvements and upgrades at smelters on the back of more stringent environmental regulations on SO2 emissions.
- Outlook: Stability in the global sulphur market and potential for improvement in processed phosphates from mid-2020 may provide support for consumption of sulphuric acid. The outlook remains stable to soft with cautious sentiment in several markets. Limited smelter outages in NW Europe are currently planned for 2020, keeping export potential healthy for the coming months.