
Australia’s nitrogen industry
An ammonium nitrate industry geared around producing explosives for the mining sector is now being joined by a major urea project and a number of renewables-based products for export of green ammonia.

An ammonium nitrate industry geared around producing explosives for the mining sector is now being joined by a major urea project and a number of renewables-based products for export of green ammonia.

QatarEnergy has announced its decision to build a new, world-scale urea production complex that will more than double Qatar’s urea production. The project is aiming to construct three ammonia production lines which will supply four new world-scale urea production trains in Mesaieed Industrial City. Total capacity for the new complex is projected to be 6.4 million t/a, more than doubling Qatar’s annual urea production from about 6 million tons per annum currently to 12.4 million tons per annum. Production from the project’s first new urea train is expected before the end of this decade.
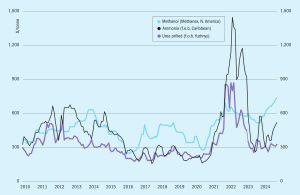
Ammonia prices could remain stable for the duration of October, with any further increases likely to be capped by a lack of demand. The outlook for November is more positive for buyers, with prices set to ease off once turnarounds at key export hubs are concluded.

In spite of increasing environmental concerns over the use of coal as a feedstock, it continues to provide around one quarter of the world’s ammonia. But in a world that is decarbonising, is there still a future for coal-based capacity?
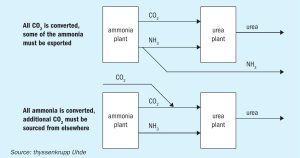
Urea revamp activities are performed to achieve improvements of the urea plant. Besides the typical capacity increase there are many options to reduce operation costs, increase plant availability or reduce environmental impact. In this article Marc Wieschalla of thyssenkrupp Uhde GmbH provides an overview of some of the options from an EPC contractor point of view.
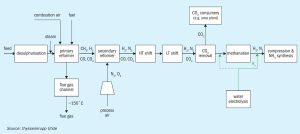
One challenge of a green revamp by stepwise injection of green hydrogen into existing ammonia/urea complexes is to cover the nitrogen demand for the ammonia synthesis while stepwise reducing the front-end load, usually by applying a cost-intensive air separation unit (ASU). thyssenkrupp Uhde GmbH has developed an advantageous concept whereby, instead of an ASU, the nitrogen gap is closed by the introduction of pretreated reformer flue gas back into the ammonia process, with the side effect to also enhance CO2 production.
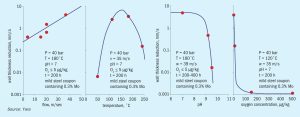
In recent years, extensive and severe internal attack has been observed of carbon steel equipment and lines in aqua ammonia service at several Yara manufacturing sites across the globe. In all cases, the damage has a distinct flow-accelerated corrosion (FAC) signature which challenges the current understanding of FAC. All features typically observed for this kind of damage mechanism, that seem to be specific to the NH3 recovery section of ammonia plant, are reported. Upgrading the material of construction for this unit, will solve this failure mode, but a leak would potentially generate health and safety problem for the release of ammonia.

One of the key challenges of producing RFNBO (renewable fuels of non-biological origin) compliant ammonia is managing the intermittency associated with renewable energy sources for hydrogen production. Furthermore, the additional costs associated with managing this intermittency can be significant. In this article, Dr Solomos Georgiou of AFRY Management Consulting explores those additional costs as well as potential ways to achieve cost savings and make RFNBO-compliant ammonia production competitive against conventional ‘grey’ ammonia.

Venkat Pattabathula, a member of the AIChE Ammonia Safety Committee, reports on the American Institute of Chemical Engineers’ (AIChE) Safety in Ammonia Plants and Related Facilities Symposium held in San Diego on 8-12 September 2024.
With a large number of green ammonia projects under development, financing remains the greatest hurdle to getting ventures off the ground.