Pathways to sustainable agriculture
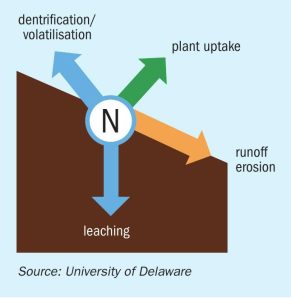
The production and use of nitrogen fertilizers are responsible for around five percent of global greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions. The fertilizer industry will need to drastically cut these emissions by 2050 as part of its contribution to the 1.5 °C global warming target. Yet around 48 percent of the global population rely on crops grown with nitrogen fertilizers. Guaranteeing food security, by continuing to supply affordable crop nutrients at scale, while transitioning to a low-carbon future, is therefore the collective challenge for the global fertilizer industry and world agriculture.