
The future of Europe’s nitrogen industry
High feedstock prices and regulatory burdens continue to put pressure on European nitrogen producers to innovate.

High feedstock prices and regulatory burdens continue to put pressure on European nitrogen producers to innovate.

New innovations, services and latest technologies to improve the operation and reliability of steam methane reformers from AMETEK Land, Kontrolltechnik, BD Energy Systems, Koch Engineered Solutions, and Quest integrity.

The COP-26 summit in Glasgow last year signed into force new rules on carbon emissions trading which may gradually start to see carbon pricing spread worldwide, with knock-on effects on emissions intensive industries like ammonia and methanol.
Argus Media’s Alistair Wallace assesses how exposed fertilizer and fertilizer raw material markets are to the conflict in Ukraine.

Improvements to equipment and materials are driving greater operational performance and higher efficiencies at urea plants. Recent advances are reviewed.

Market Insight courtesy of Argus Media

EuroChem has made a binding offer for Borealis Group’s fertilizer, melamine and technical nitrogen business.

German slurry handling specialist Vogelsang has just launched a new acidification technology which it claims will reduce ammonia emissions from agriculture, reducing up to 70% of ammonia to nutrient rich ammonium. Its new SyreN technology is an onboard sulphuric acid dosing system for tractors that treats slurry or digestate as it is applied to the land. It uses a front-linkage mounted unit to carry the acid, which also improves tractor weight distribution. The acid is dosed when the organic fertiliser is fed to the applicator, with a pH regulator automatically controlling and adjusting the flow. Nitrogen uptake of organic fertilizer is also increased by up to 1/3 as the ammonium is more easily metabolised by the soil. Results from a study in Germany showed that the acidifying slurry increased crop yield by up to 20%. The sulphur contained in the acid also becomes available to the plants as sulphate after spreading, eliminating the need for an additional pass over the field to administer a supplementary sulphur fertiliser, such as ammonium sulphate nitrate. At approximately 30 kg/ha, the amount of sulphur introduced into the crop with the SyreN system corresponds to the average amount of sulphur that is already applied to crops in the course of a growing season.
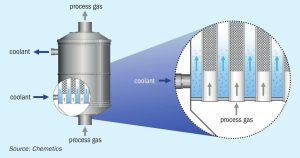
With climate change looming there is an increased focus on reducing the environmental footprint of the production of fertilizers. The use of renewable energy/green hydrogen is one way to make the fertilizer industry more environmentally sustainable. In this article, Rene Dijkstra of Chemetics introduces the Green Fertilizer Complex. This practical solution integrates an oxygen-based sulphuric acid plant using the Chemetics’ patented CORE-SO2™ process with a green hydrogen and ammonia facility to deliver low cost, low emission, and carbon-free phosphate (MAP/DAP) and/or sulphate (AMS) based ammonia fertilizers.
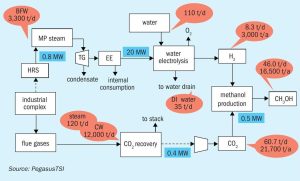
Ricardo L. Sepulveda of PegasusTSI reviews options to decrease the CO2 footprint of a fertilizer industrial complex and illustrates the technical and economic feasibility of utilising clean energy from a sulphuric acid plant in a fertilizer complex to produce green hydrogen, which in turn can be used to produce green methanol or green ammonia.