
The year ahead: affordability and availability concerns
We look ahead at fertilizer industry prospects for the next 12 months, including the key economic and agricultural drivers likely to shape the market during 2022.

We look ahead at fertilizer industry prospects for the next 12 months, including the key economic and agricultural drivers likely to shape the market during 2022.

State-of-the art technologies offered by thyssenkrupp, Casale and Stamicarbon are helping make nitrates production more secure and sustainable.

Yara and Lantmännen have signed an agreement to bring fossil-free mineral fertilizers to market.

The production of syngas from hydrocarbon feedstock uses a number of catalytic steps to increase efficiency and maximise conversion while minimising energy consumption. In this article we report on the latest developments in water gas shift catalysis from Johnson Matthey, Clariant and Topsoe, and shift converter design from Casale.

As a quick glance through the Index of last year’s articles and news items in this issue of the magazine will amply demonstrate, 2021 was a year full of project announcements for low carbon ammonia and methanol projects of all hues; blue, green, turquoise and many other shades besides. Market analysts CRU said in December that they calculated that there have been a total of 124 million t/a of low carbon ammonia projects announced, 80 million t/a of which came in 2021 alone, equivalent to 55% of current ammonia capacity. These range from tentative pilot plants that are fully costed and often with government grants already secured to blue sky visions of vast electrolysis hubs in the deserts of Arabia with timescales towards the end of the decade – it’s often the case that the longer the proposed timescale, the less likely a project is to happen.
The International Fertilizer Association (IFA) has signed a memorandum of understanding with the United Nations Food and Agriculture Organisation (FAO) over collaboration to support the FAO’s vision of transformative change and innovation in agriculture. Svein Tore Holsether, IFA Chair, signed the agreement at a live virtual signing in December together with FAO deputy director general Beth Bechdol. The agreement outlines collaboration to further shared goals and objectives with regard to the promotion of sustainable food and agriculture. Both parties will work together to raise awareness about the International Code of Conduct for the Sustainable Use and Management of Fertilizers (Fertilizer Code), promote education and knowledge transfer and continue their successful collaboration on fertilizer statistics.
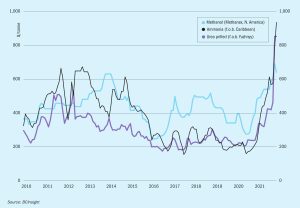
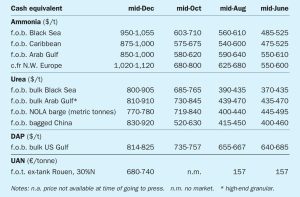
The ammonia market has entered 2022 looking very different to last year, with early January Pivdenny prices $875/t higher on a mid-point basis than they were at the start of 2021, and the likelihood of further gains ahead.
Market Insight courtesy of Argus Media
The Bia Energy Operating Company says that it is evaluating a $550 million blue methanol plant at the port of Caddo-Bossier in Shreveport, Louisiana. The unit would have a capacity of 530,000 t/a of methanol using natural gas feedstock with downstream carbon capture, reducing CO2 emissions by more than 90% compared to other methanol plants. The company is expected to make a final decision in 1Q 2022, with construction expected to last approximately two years, and commercial operations to begin soon after.

Recent spikes in natural gas prices, particularly in Europe, have highlighted the tightness of natural gas markets around the world going into the northern hemisphere winter. Are ammonia and methanol producers on for a run of high gas prices in 2022?