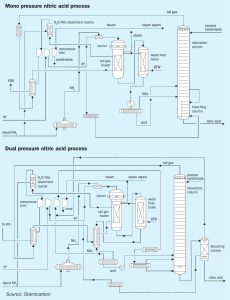
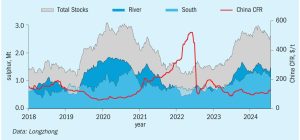
Nitrogen Industry News Roundup
OCI Global says that it has reached an agreement for the sale of 100% of its equity interests in its Clean Ammonia project currently under construction in Beaumont, Texas for $2.35 billion on a cash and debt free basis. The buyer is Australian LNG and energy company Woodside Energy Group Ltd. Woodside will pay 80% of the purchase price to OCI at closing of the transaction, with the balance payable at project completion, according to agreed terms and conditions. OCI will continue to manage the construction, commissioning and startup of the facility and will continue to direct the contractors until the project is fully staffed and operational, at which point it will hand it over to Woodside. The transaction is expected to close in H2 2024, subject to shareholder approval.