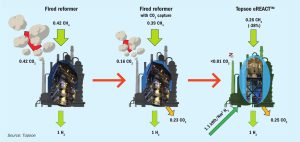
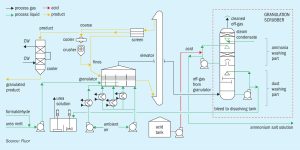
Nitrogen Industry News Roundup
BASF says that its high-pressure regenerative CO2 capture technology HiPACT ® , codeveloped by BASF and engineering partner JGC Corporation will be used by INPEX, one of Japan’s largest exploration and production companies, in its Kashiwazaki Clean Hydrogen/Ammonia Project. This is Japan’s first demonstration project for the production of blue hydrogen/ammonia from domestically produced natural gas, the consistent implementation of carbon capture, utilisation and storage (CCUS) in domestic depleted gas fields and the use of hydrogen for power generation and ammonia production. The project is funded by the Japanese governmental organization New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organization (NEDO).