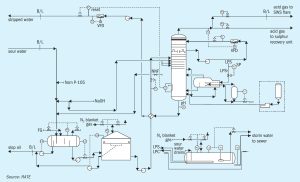
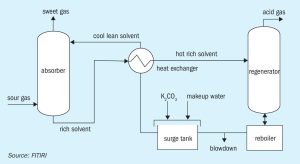
OCI subsidiary Fertiglobe says that it has partnered with the Abu Dhabi National Oil Company (ADNOC), to enable the sale by ADNOC of the first cargo of blue ammonia to Itochu in Japan, for use in fertilizer production. Fertiglobe, a 58% − 42% partnership between OCI and ADNOC respectively, will produce the blue ammonia at its Fertil plant at Ruwais in Abu Dhabi for delivery to ADNOC’s customers in Japan. This represent the first production milestone of a planned scale-up of blue ammonia production capabilities in Abu Dhabi, which is expected to include a low-cost debottlenecking program at Fertil. In addition, it was announced in June that Fertiglobe will join ADNOC and sovereign wealth fund ADQ as a partner in a new world-scale 1.0 million t/a blue ammonia project at Ta’Ziz in Ruwais, subject to regulatory approvals. The design contract for this project has been awarded, with a final investment decision expected in 2022 and start-up targeted for 2025. A feasibility study was also agreed in July betweenh the state-owned Japan Oil, Gas and Metals National Corp. (Jogmec), Inpex and JERA as well as ADNOC to explore the possibility of producing 1.0 million t/a of blue ammonia in Abu Dhabi and transporting it to Japan.