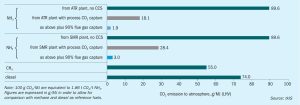
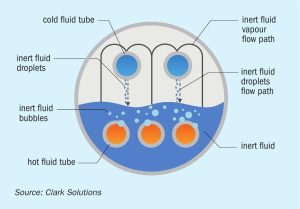
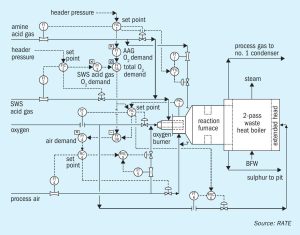
Syngas News Roundup
A recent report from BloombergNEF (New Energy Foundation) looking ahead to 2050 argues that green hydrogen can be cheaper than natural gas. It finds that ‘green’ hydrogen from renewables should become cheaper than natural gas (on an energy-equivalent basis) by 2050 in 15 of the 28 markets modelled, assuming scale-up continues. These countries accounted for one-third of global GDP in 2019. In all of the markets BNEF modelled, ‘green’ hydrogen should also become cheaper than both ‘blue’ hydrogen (from fossil fuels with carbon capture and storage – CCS) and even ‘grey’ hydrogen from fossil fuels without CCS. The cost of producing ‘green’ hydrogen from renewable electricity should fall by up to 85% from today to 2050, the report predicts, leading to costs below $1/kg ($7.4/MMBtu) by 2050 in most markets. These costs are 13% lower than BNEF’s previous 2030 forecast and 17% lower than their previous 2050 forecast. Falling costs of solar photovoltaic (PV) electricity are the key driver behind the reduction; BNEF now believes that PV electricity will be 40% cheaper in 2050 than they had thought just two years ago, driven by more automatic manufacturing, less silicon and silver consumption, higher photovoltaic efficiency of solar cells, and greater yields using bifacial panels.