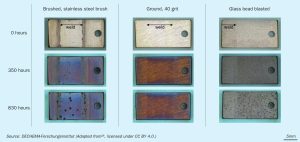
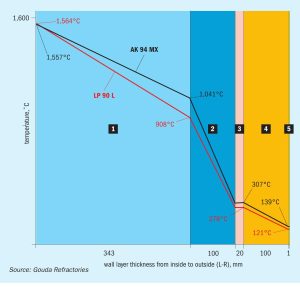
Reliability of reformer outlet systems
The reliability of primary reformers is a key issue for syngas plants. Quest Integrity describes the damage mechanisms and material limitations that impact the reliability of reformer outlet systems and the improvements that may be implemented.