Decentralised small scale methanol plants
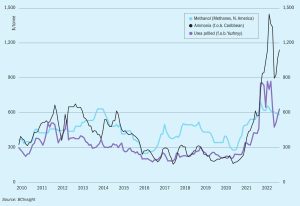
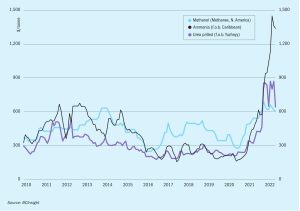
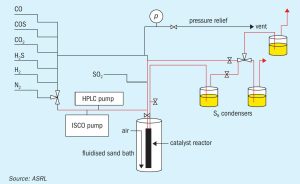
Air Liquide presents the results of an internal study to identify preferred natural gas-based plant configurations at a methanol capacity of 250 t/d. Delivering small capacity plants requires a focus on the total cost of ownership (TCO) for the economics to be successful, in addition to the CO 2 footprint of the operation. As found by this study, SMR concepts are naturally power balanced for standalone greenfield operations and show no particular advantage for power import in a brownfield setting. POX and ATR cases are greatly improved and even advantaged in a brownfield setting compared to SMR when shifting from power balance to power import cases.