
IMTOF 2025
This year’s International Methanol Technology Operators’ Forum (IMTOF) was held at the Holiday Inn Regents Park hotel, London, from June 15 to 18.

This year’s International Methanol Technology Operators’ Forum (IMTOF) was held at the Holiday Inn Regents Park hotel, London, from June 15 to 18.

Casale is specialised in revamping natural gas-based methanol plants. Decarbonisation of methanol plants is a goal for many producers achievable with a proper revamping strategy. Pietro Moreo of Casale discusses how Casale’s innovative technologies and extensive experience ensure reliable efficient capacity and performance enhancements together with CO2 emissions reduction tailored to meet revamping project targets.

The production of methanol from waste offers a groundbreaking solution for sustainable urban waste management as well as producing an alternative renewable fuel for maritime transport. Giacomo Rispoli, Andrea Angeletti and Alessia Borgogna of Nextchem provide an overview of the waste conversion process and its application.

No longer viewed as only a chemical feedstock, methanol is increasingly being regarded as a low-carbon energy carrier. Zinovia Skoufa of Johnson Matthey discusses the role of sustainable methanol as a multi-pathway fuel for the energy transition.

NextChem (Maire) awarded contract for basic engineering and supply of critical proprietary equipment for the 'Pacifico Mexinol' ultra-low methanol project in Mexico

It is with great sadness that we report the death of Dr. Umberto Zardi, who passed away on March 17th 2025 at his home in Breganzona, Lugano, Switzerland. Dr Zardi was an innovator in the nitrogen industry and for many years the president and driving force behind Ammonia Casale, now simply Casale SA, becoming responsible for its revival and transformation into the global engineering and technology giant that it is today.
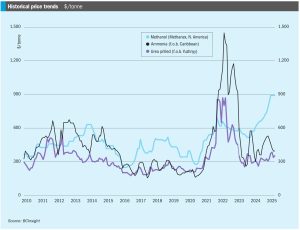
• Continuing oversupply means that ammonia prices should continue to come under pressure moving into 2H April, though it remains to be seen just how much further values in Asia can decline before producers begin to shutter output.

Methanol demand is rising again after a few years of relative stagnation, but with the Chinese MTO boom largely over, it looks to be energy uses which will drive most future demand.

NextChem subsidiary KT Tech has been awarded a licensing contract for the implementation of NextChem’s proprietary NX AdWinMethanol® Zero technology for Pacifico Mexinol, an ultra-low carbon methanol facility near Los Mochis, Sinaloa, on the Pacific coast of Mexico, which will have a planned output in excess of 2.1 million t/a. Transition Industries LLC, based in Houston, Texas, is developing Pacifico Mexinol with the International Finance Corporation (IFC), a member of the World Bank Group. When it initiates operation in 2028, Pacifico Mexinol is expected to be the largest single ultra-low carbon methanol facility in the world – producing approximately 350,000 t/a of green methanol and 1.8 million t/a of blue methanol annually from natural gas with carbon capture.The value of the licensing award is in the low tens of million euros, with the whole package estimated to be about e250 million, including basic engineering, proprietary and critical equipment supply, as well as assistance to commissioning, start-up and operation of the facility.

Clariant says that its MegaMax 900 methanol synthesis catalyst has been used in the successful startup of European Energy’s green methanol plant at Kasso, Denmark. The facility uses biogenic CO2 and green hydrogen to produce up to 42,000 t/a of green methanol. Clariant’s Applied Catalyst Technology (ACT) technical service team provided on-site support throughout the startup procedure, overseeing the catalyst loading, reduction, and startup. Clariant says that the catalyst is operating with excellent activity and stability despite the challenging conditions of CO2 -to-methanol conversion.