The year that went viral
A look back at some of the major events of 2020 for the sulphur and sulphuric acid industries, as well as a look forward as to how 2021 might look.

A look back at some of the major events of 2020 for the sulphur and sulphuric acid industries, as well as a look forward as to how 2021 might look.

Demand for oil in developed countries was already falling before the coronavirus outbreak, and consumption growth is slowing in the developing world. Peak oil demand may arrive in the next decade. Coupled with more reinjection of sour gas rather than sulphur extraction, could we be seeing falling elemental sulphur production in a decade or so?
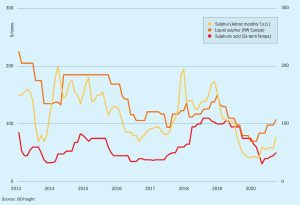
Production cuts globally at refineries have left supply tight heading into the fourth quarter, firming prices. This has been compounded by major exporters in the Middle East prioritising sulphur tonnes to contracts before spot sales.
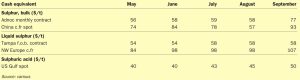
Matt Langworthy, Analsyt for Argus Media, assesses price trends and the market outlook for sulphur.

Market Insight courtesy of Argus Media

The late autumn gloom has darkened in recent weeks, as Europe slipped back into a lockdown that seemed as inevitable as the encroaching winter.

With around 90 percent of global trade requiring sea transport, shipping remains the life blood of the world economy. Intercontinental trade, the bulk transport of raw materials, and the import/export of food and manufactured goods all rely on affordable and effective shipping.
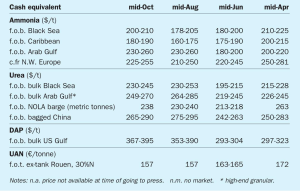
Alistair Wallace , Head of Fertilizer Research, Argus Media, assesses price trends and the market outlook for nitrogen.

Ammonia prices have been on a rising trend over the past few months as plant closures begin to make themselves felt. Yara’s Baltic ammonia price also rose sharply at the start of October, and Nutrien’s announcement of the closure of its PCS-03 plant on Trinidad helped lift prices, with Yara and Mosaic’s contract prices rising $16/t in October.

Market Insight courtesy of Argus Media