
Potash project listing 2021
Fertilizer International presents a global round-up of current potash projects.

Fertilizer International presents a global round-up of current potash projects.

New innovations and the latest equipment options from FEECO International, Casale, thyssenkrupp Fertilizer Technology and Eirich are helping to perfect the fertilizer finishing process.

Polysulphate is a new multi-nutrient fertilizer mined in the UK. Its unique characteristics and mix of nutrients make it especially suitable for potato crops, explains Patricia Imas, chief agronomist at ICL Innovative Ag Solutions (IAS).

Market Insight courtesy of Argus Media

With globalisation seemingly in retreat, the protectionist impulse is seeing a rise in barriers to trade, from quotas and tariffs to anti-dumping actions and domestic subsidies.

Reducing carbon footprint in the synthesis of chemicals is a new challenge, a necessary requirement in the pursuit of sustainable products designed to minimise environmental impacts during their whole lifecycle. So-called “green” technologies for ammonia, methanol and hydrogen are being developed to meet these challenges. Casale, Linde, thyssenkrupp Industrial Solutions, Toyo Engineering Corporation, Haldor Topsoe and Stamicarbon report on some of their latest developments.

Rapidly escalating natural gas prices forced plant closures across Europe during September. Worst affected was the UK, where a fire at a cross-Channel electricity cable and low output from wind energy has, combined with low domestic storage capacity led to a surge in demand for gas for power stations and wholesale gas prices reached a record 350 pence per therm (equivalent to $46/ MMBtu) in October. On September 15th, CF Industries announced that it was halting operations at both its Billingham and Ince fertilizer plans due to high gas prices. Although ammonia prices have also risen, they have not kept pace with gas price rises, and there is a limit to what farmers could be expected to pay. CF CEO Anthony Will said: “$900 is the gas cost in a tonne of ammonia and the last trade in the ammonia market that was done was $700 a tonne”. As these plants supply most of the UK’s carbon dioxide for food and drink manufacture, the government said it would provide “limited financial support” to keep the Billingham plant operational, and that plant re-started on September 21st. Meanwhile, BASF closed its Antwerp and Ludwigshafen plants in Belgium and Germany due to what the company called “extremely challenging” economics. Fertiberia ceased production at its Palos de la Frontera site in Spain, and Puertellano remained down for scheduled maintenance. Yara shut 40% of its European ammonia production in September, and OCI partially closed its Geleen plant in the Netherlands. Achema in Lithuania decided against restarting its ammonia plant following maintenance in August, and OPZ in Ukraine shut one ammonia line at Odessa, with Ostchem and DniproAzot likely to follow. Borealis in Austria also reduced production.
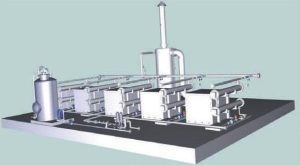
Nitrogen-rich wastewaters remain a major issue for fertilizer and other industries. Saipem’s new electrochemical technology, SPELL, is an important step towards the overall objective of zero industrial pollution. A complete engineering review of the technology, its alignment with all international applicable standards, and optimisation has now been concluded and the technology is ready for deployment for the removal of ammonium nitrogen from industrial waters and wastewaters. Saipem discusses the key features of SPELL and reports on the first two industrial references.

As sulphur recovery units operate at progressively higher temperatures, creep stress in the furnace refractory lining can lead to deformation or even failure of the bricks and require the shutdown of the SRU. UK-based DSF Refractories have developed a product which minimises creep stress damage at high temperatures, for a longer-lived furnace lining.

RSK and its subsidiary ADAS have developed a sustainable solution for the disposal of sulphur waste generated from a natural gas processing facility in Iraq. C. Teulon of RSK reports on the research that was carried out to test whether the waste sulphur from a biological sulphur removal process could be applied in agriculture to increase the quality and quantity of crops in Iraq.