
The challenges facing refiners
The refining industry, the source of half of the world’s elemental sulphur, continues to face major structural changes from changing feedstock and product slates and increasing regulatory burdens.

The refining industry, the source of half of the world’s elemental sulphur, continues to face major structural changes from changing feedstock and product slates and increasing regulatory burdens.

Using case studies of a refinery amine unit and a sour water stripper (SWS), U. M. Sridhar of Three Ten Initiative Technologies LLP, N. A. Hatcher and R. H. Weiland of Optimized Gas Treating Inc. demonstrate the capabilities of a mechanistic, chemistry-based, truly predictive model for calculating corrosion rates for various amines and for sour water. At a time when asset integrity is much sought after, the utility of this fully predictive model is to prevent failures before they occur, rationally select materials of construction, enhance plant safety, and mitigate risk.

After a poor 2019, when global demand contracted by nearly 2.5%, phosphate markets are expected to rebound in 2020. Saudi Arabia and Morocco dominate new capacity additions while India and Brazil continue to be the key importers. US and Chinese production is in slow decline, meanwhile.
Sulphuric acid plant operators juggle multiple issues trying to keep their plants running efficiently and reliably. With the revolutionary ClearView™ process health monitoring solution, as well the DynSOx™ software for simulating dynamic operation, Haldor Topsoe strives to bring digital services with real and tangible operational benefits to the sulphuric acid industry. P. Szafran and M. Granroth discuss how together these digital services can help acid plant operators meet their daily targets.

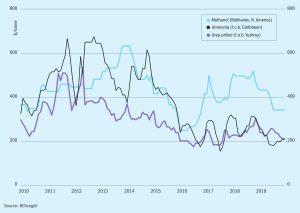
Floor prices in nitrogen markets are set by marginal producers high on the cost curve, usually using higher cost feedstocks. Recently, lower coal prices in China and the cost of imported LNG have begun to change the dynamic between producers on the margins.

‘Green’ methanol means many things to different people. It encompasses low carbon emissions methanol manufacture at scale, recovery of material through waste gasification and conversion to methanol and power to liquid (e-fuel) methanol via electrochemistry and sometimes a combination of all of the above. Each route has a place in reducing the overall carbon footprint of production and subsequent use of methanol, driven by both governmental incentives or societal demand. In this article Andrew Fenwick of Johnson Matthey reviews the various routes to manufacture.
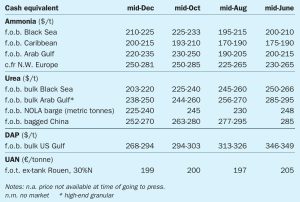
Alistair Wallace , Head of Fertilizer Research, Argus Media, assesses price trends and the market outlook for nitrogen.
US agricultural demand is expected to pick up in 1Q 2020, and farm inventories are low.
CRU’s Nitrogen + Syngas conference and exhibition takes place this year at the World Forum, The Hague, in The Netherlands, from 17 to 19 February 2020.
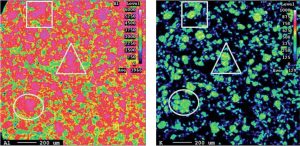
M. Wilson, J. Brightling and M. Carlsson of Johnson Matthey detail the development of steam reforming catalyst, with a focus on an operating case study, where Johnson Matthey has combined pelleted and structured reforming catalysts to deliver additional value from an existing asset.