
Sulphur dust suppression
Sulphur dust is one of the greatest hazards when producing and handling solid sulphur, and methods for its suppression are vitally important to prevent fire and explosion.

Sulphur dust is one of the greatest hazards when producing and handling solid sulphur, and methods for its suppression are vitally important to prevent fire and explosion.

The modern sulphur industry is in effect a response to the environmental problems created by the presence of sulphur compounds in oil and gas, and the consequent release of sulphur dioxide when they are burned. The tens of millions of tonnes extracted, formed, traded and used for sulphuric acid production every year would otherwise be entering the atmosphere and causing health issues, especially in major cities, or returning as acid rain. One of the most recent step changes in sulphur recovery has come from the extension of rules on sulphur content of fuels that have been commonplace for road vehicles for many years into the maritime transport sphere. The International Maritime Organisation has mandated a reduction in sulphur content of bunker fuels to 0.5% worldwide, and 0.1% in busy shipping regions that have become designated emissions control areas (ECAs). Because bunker fuels were made from refinery residues, they often had high concentrations of sulphur in them; the limit before 2020 was 3.5%. As a result, a recent paper by two climate scientists calculates that global SO2 emissions have dropped by as much as 10% since 2020 because of the IMO limits. Given that atmospheric sulphur dioxide is responsible for an estimated 20-90,000 preventable deaths per year, this is surely a good thing.

Worley has been awarded a contract to supply Chemetics’ CORESO2™ technology for a sulphuric acid plant and associated oxygen unit at the Arafura Rare Earths project, sited 135 km north of Alice Springs in Australia’s Northern Territory. A greenfield mine will extract and process neodymium and praseodymium to create ultra-strong permanent magnets for a range of applications, such as household electronics and high-performance motors for electric vehicles.

Most processes involving sulphur, from smelting to refining, produce sulphur dioxide as a by-product. Regulations continue to tighten on industrial SO2 emissions worldwide, leading to greater recovery of sulphur and sulphuric acid at these sites.

Sulphur is a vital secondary crop nutrient. It can be delivered in sulphate, thiosulphate and elemental form. The range of product and process options are outlined.

It has long been known that sulphur dioxide aerosols can reflect sunlight back into space. On a large scale, this has tended to come from volcanic eruptions. The explosion of the island of Krakatoa in 1815 led to the following year, 1816, becoming known in Europe as ‘the year without a summer’. More recently, it is estimated that the eruption of Mount Pinatubo in the Philippines in 1991, the second largest eruption of the 20th century, sent around 18 million tonnes of SO2 into the stratosphere. Temperatures in the troposphere – the atmospheric layer closest to the earth – dropped by about 0.5°C as a result for about two years afterwards.

Sulphur is a relatively safe and inert solid. However, it has a number of unique physical and chemical properties which can give rise to hazards, particularly during transport and handling.

A move towards so-called ‘sustainable aviation fuels’ (SAF) could see refineries having to recast their operations. What might this mean for sulphur production?

By recovering waste heat as process steam or electrical energy, technologies are available that can help sulphuric acid plants meet their energy goals. Colin Shore of Elessent Clean Technologies discusses how MECS® HRS™ technology can offer a sustainable solution to enhance sulphuric acid plant performance, while lowering its carbon emissions.
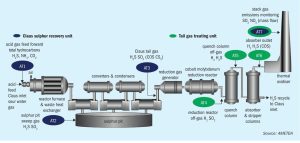
Jochen Geiger of AMETEK Process Instruments reviews SRU process analyser standards, how to choose the right instruments, what to watch out for when selecting the point of installation, responsibilities for the analysers after installation, and how to make best use of the information provided by these analysers. Potential upset conditions and how analysers can help us to understand and mitigate them are also discussed.