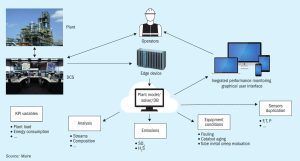
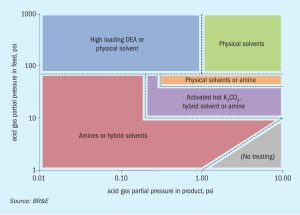
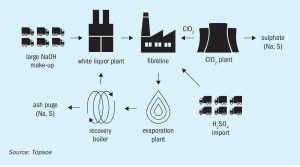
Channelling in SRU converters
This troubleshooting case study describes an incident at one of the sulphur recovery units at BPCL Kochi Refinery, India. Following a maintenance turnaround of the unit in 2022, unusually high H2 S and SO2 were observed at the outlet of the Claus section. This created an additional load on the tail gas reactor, which led to frequent plugging in the quench column and frequent outages in the tail gas unit, creating environmental and reliability issues in the unit. The activities to identify the root cause of the incident are described and the measures to solve the problem are shared.