Ultra capacity with ultra low emissions
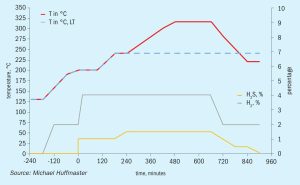
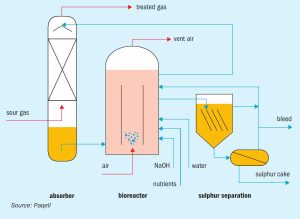
As environmental SO2 emission regulations become more stringent, tail gas treating options become limited. To potentially achieve lower opex and improved plot plan, utilising a biological desulphurisation process as an alternative to a conventional amine-based TGT unit is becoming of increased interest in the oil and gas industry. At the same time, demands for increased SRU capacity and reliability favour the use of medium and high-level oxygen enrichment.