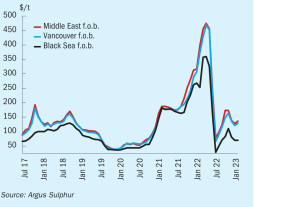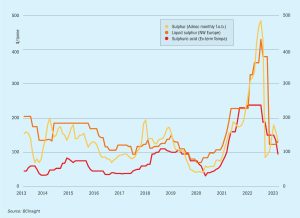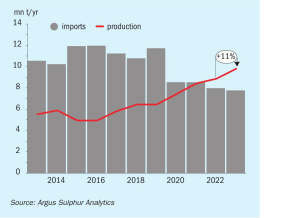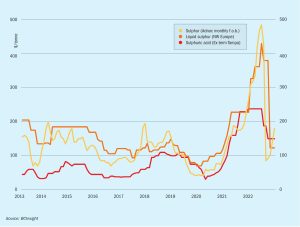
Sulphuric Acid News Roundup
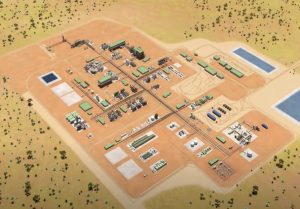
Arafura Rare Earths Ltd has awarded Worley subsidiary Chemetics Inc the contract to install Chemetics CORE-SO2™ sulphuric acid technology at its Nolans Project in the Northern Territory of Australia. The scope of the contract is to deliver the detailed engineering and supply of the sulphuric acid plant plus associated oxygen plant on a lump sum basis. The acid plant at Arafura’s Nolans Project will be designed to meet future emission performance and clean energy transition goals, utilising CORE-SO2’s high turndown capability and the potential to idle the plant while keeping the catalyst warm for extended periods of time, allowing the acid plant to operate with 95% reduced SO 2 emissions when compared to traditional double contact double absorption (DCDA) plants. High pressure steam production within the process will allow CO 2 - free electrical power to be generated. By removing the use of a diesel or natural gas start-up burner, further greenhouse gas emissions will be prevented.