
Price Trends
Market Insight courtesy of Argus Media

Market Insight courtesy of Argus Media

Leaks in the high-pressure synthesis section of a urea plant can have catastrophic consequences. UreaKnowHow.com started to collect incidents in an incident database and in 2017 AmmoniaKnowHow.com and UreaKnowHow.com introduced FIORDA, the Fertilizer Industry Operational Risk Database, a global open source risk register for ammonia and urea plants.
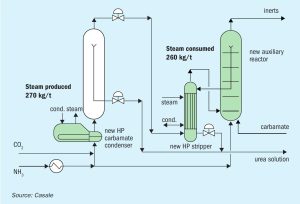
Casale reviews urea plant revamping process schemes and successful case studies for energy savings and TOYO discusses its latest revamping technologies including application of the new generation low-pressure, energy-saving ACES21-LP™ process.
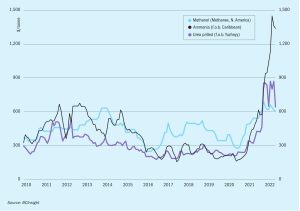
Overall the market finds itself in a period of illiquidity, and is exposed to further uncertainty in 4Q because of the European energy crisis. Spiralling natural gas costs in Europe, with Dutch TTF gas prices trading around e200/MWh, are forcing European fertilizer producers to close ammonia capacity and buy in from overseas.

The war in Ukraine has severely affected the supply of ammonium nitrate and CAN from Russia and Ukraine, with particular potential impact on Europe and Latin America. Can urea make up the difference?
A record rise in gas prices at the end of August triggered a spate of ammonia production curtailments across Europe. These included major shutdown announcements from CF Fertilisers UK, Grupa Azoty, Yara International and others.

Producing efficient fertilizers that deliver nutrients directly to crops in exactly the right amounts has clear economic and environmental benefits. Recent advances in controlled-release and stabilised fertilizer technology are highlighted.

ICL has developed a new generation of rapid biodegradable coatings for its controlled-release fertilizer (CRF) portfolio. The new coating technology reduces the environmental footprint of CRFs and will help farmers meet the requirements of Europe’s Green Deal. This patented innovation, named eqo.x, coats nitrogen fertilizers for field grown crops. Eqo.x has already been fully tested in the field – and shows excellent results in terms of production, nutrient use efficiency, volatilisation and leaching reduction. Ronald Clemens, ICL Global Marketing & Portfolio Manager CRF, explains the benefits.
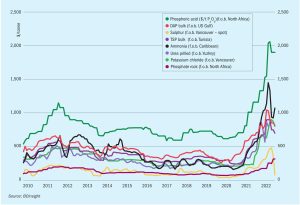
Market Insight courtesy of Argus Media

It is generally necessary to solidify sulphur into a robust form suitable for handling and long-distance transport. Granulation, pastillation and prilling are some of the technologies used to produce solid sulphur from molten material. Similar technologies are also used to manufacture sulphur fertilizers.