Market Outlook
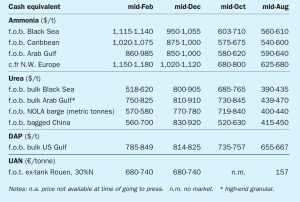
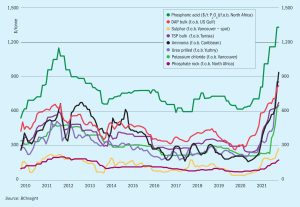
The ammonia market, already seeing record pricing in the wake of the winter’s gas price squeeze, is braced for even higher pricing in the wake of the Russian invasion of Ukraine. The impact upon gas prices has been most marked, with rates of over $65/MMBtu seen in European forward pricing as the threat of a cessation of Russian gas exports loomed. This will undoubtedly lead to widespread idling of ammonia capacity in Europe.