Sulphur 388 May-Jun 2020

31 May 2020
Upgrade of Claus TGTUs
CLAUS TAIL GAS TREATING
Upgrade of Claus TGTUs
BASF has developed a new generation of promoter system compatible with MDEA solutions named OASE® yellow. The new promoter system increases the selectivity and capacity of the amine solvent, resulting in improved performance of tail gas treating units and allowing the processing of more sour crudes. A. Kern and G. Vorberg of BASF discuss two case studies demonstrating the benefits of OASE yellow.
Refinery sulphur recovery units (SRUs) are faced with the challenge of processing increasingly sour crudes, while maintaining, or even reducing, the level of sulphur emissions.
Higher sulphur loads need to be treated by the Claus process and its tail gas treatment section. As a first measure, operators are exploring various ways to improve the performance of the SRU without incurring the additional costs required for revamping.
Replacing the common MDEA-based amine solution in the Claus TGTU can provide a very cost-effective option, not only reducing emissions, but also allowing significant opex savings as illustrated in this article.
MDEA-based amine solvent in TGTUs
Methyl-diethanolamine (MDEA) is a tertiary amine, widely used in SRU TGTUs because of its natural selectivity towards the removal of H2 S. However, it is reaching its limits for more advanced acid gas removal requirements.
First generations of promoter systems (mainly comprising inorganic acid compounds) have been introduced. This so-called “acidification” of MDEA reduces the pH value of the amine solution, which is beneficial for the regeneration step, but has a negative effect on the absorption capacity of the amine. It allows a lower residual acid gas lean loading of the amine. As a result, lower H2 S concentrations and therefore sulphur emission reduction is achievable at lower reboiler duties for regeneration.
However, acidified MDEA is lacking with regard to absorption capacity and can lose its benefits when more sour crude is being processed in the refineries leading to much higher sulphur loads to the SRU and the respective tail gas sections. In addition, such systems are more prone to corrosion incidents due to the (too) low residual acid gas lean loading of the amine adversely affecting the corrosion protective layers build up during plant operation.
To overcome these constraints, BASF has developed a new generation of promoter system compatible with MDEA solutions, named OASE yellow, providing an amine solvent with high selectivity and high capacity.
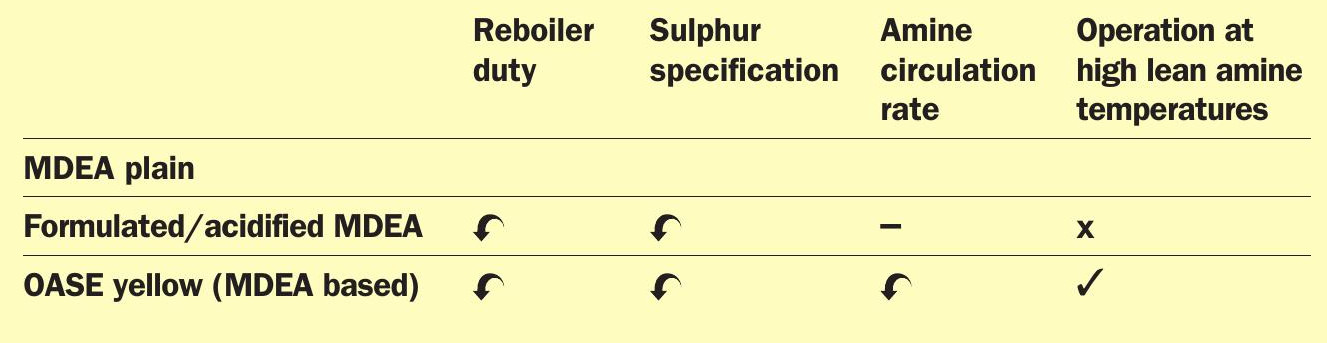
An overview of selective MDEA-based amine formulations available and used in tail gas treatment units is shown in Table 1.
Reduction of reboiler duty for the regeneration of the amine solution translates into opex savings. Reduction of the amine circulation rate also translates into opex savings with regard to the power consumption of the amine pumps.
The new generation, high selectivity, high capacity MDEA formulation can offer both.
Case studies
The following two case studies demonstrate the benefits of running the TGTU on the new high selectivity and high capacity amine solvent after successful introduction of the innovative OASE yellow promoter to existing MDEA systems.
Both conversions are carried out during 100% plant load, meaning no plant shutdown and no process interruption.
Case study 1 – A German refinery
This case study describes a commercial refinery TGTU, previously running on MDEA, which converted to OASE yellow with the aim to reduce sulphur emissions.
The tail gas to the amine absorber has a H2 S content of 1.2 vol-% and a CO2 concentration of around 30 vol-%.
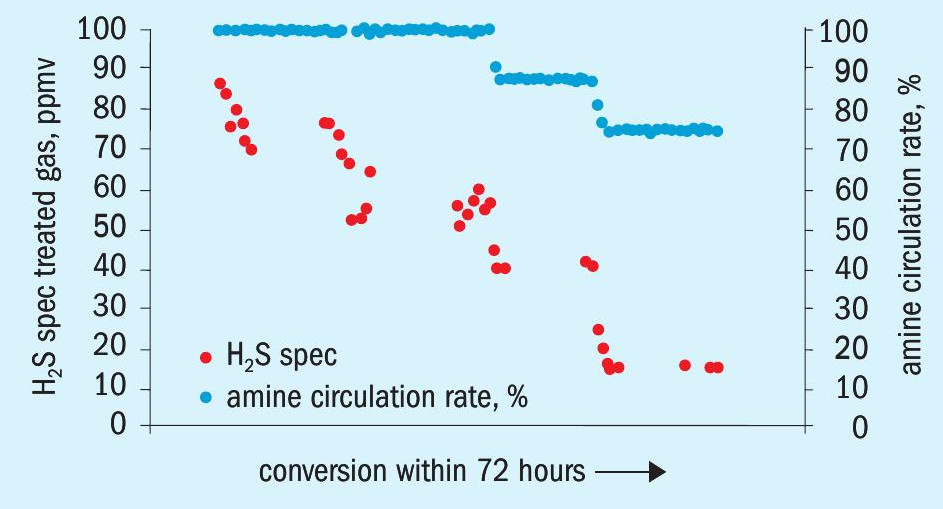
Within a timeframe of 72 hours the OASE yellow promoter was dosed into the TGTU amine loop by using a small dosing pump. While the unit was running at full capacity, new operational settings were adjusted accordingly, and the process was optimised.
The effect of the amine conversion was visible instantaneously: The H2 S concentration in the treated gas leaving the amine absorber and passing to the flare decreased from 90 ppmv (start of the OASE yellow promoter addition) down to 15 ppmv (end of the OASE yellow promoter addition).
Overall, the SO2 emission of the SRU TGTU system was reduced by 80%.
In parallel, the increased specific absorption capacity of the solvent allowed the amine circulation rate to be reduced by >25%. Fig. 1 summarises these findings.
In a later optimisation stage, the lean amine temperature was raised to the feed gas temperature in order to achieve an almost neutral water balance and subsequently no reflux bleed stream. The amine losses were thereby much reduced.
Case study 2 – A Korean refinery
In this case study a commercial refinery TGTU previously running on acidified MDEA solution was converted to OASE yellow with the aim to reduce opex costs.
Due to oxygen enrichment in the burner operation of the sulphur recovery unit, the tail gas to the amine absorber has a high H2 S content of 6.8 vol-%. The CO2 concentration is 3.5 vol-%.
When processing more sour crude the sulphur emission can exceed the maximum emission levels allowed. This can happen especially during hot summer months when lean amine temperatures are increasing (e.g. due to limited air cooler duty) leading to violation of the TGTU treated gas H2 S spec. The OASE yellow system shows little temperature sensitivity providing another advantage compared to MDEA solutions.
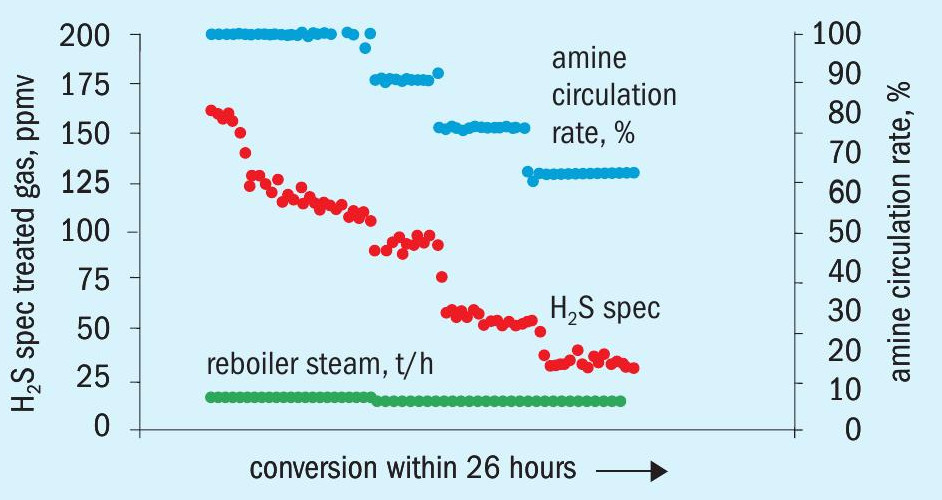
Before OASE yellow promoter was introduced to the TGTU amine loop, the treated off gas going to the stack had an H2 S concentration of 165 ppmv. The flow rate of tail gas to the absorber was 10,030 Nm3 /h.
The conversion was completed within 26 hours and the H2 S concentration in the off-gas dropped to 35 ppmv. Meanwhile, the amine circulation rate was reduced by >30%. Fig. 2 is illustrates the conversion process.
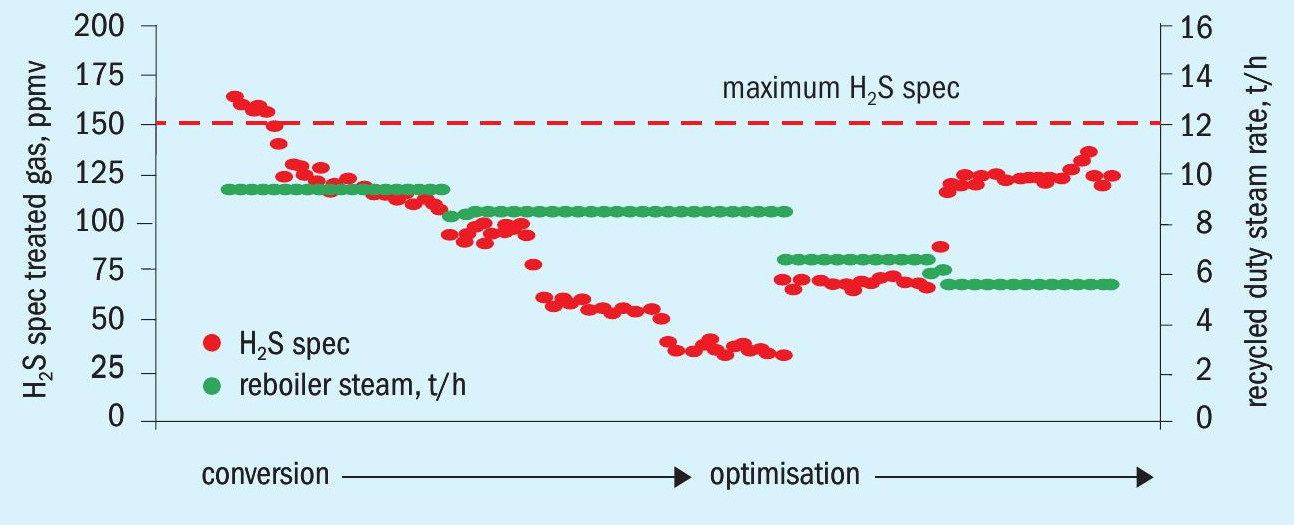
In a second step, following the conversion, the optimisation phase started focusing on opex savings. A key driver for lower energy consumption and related cost is the reduction of the low-pressure steam used to regenerate the amine solution.
Without changes in the gas flow rates and its composition, the steam flow to the reboiler was step-wise reduced starting with 9.4 t/h. This in turn increased the H2 S concentration in the treated tail gas. However, the H2 S spec of maximum 150 ppmv can still be achieved while significantly reducing steam flow to 5.5 t/h. This translates into an outstanding steam saving of 4 t/h (-40%).
In addition, since the conversion of the amine system the plant has been able to run at 5-10 K higher lean amine temperatures, while still achieving the H2 S spec. In combination with the reduced amine flow rate, total lean amine cooling duty has been lowered to such an extent that the lean amine air cooler is no longer required and the plant is running a small amine water cooler in its place.
Fig. 3 summarises provides data for the optimisation process following the amine conversion.
Results and discussion
The upgrade i.e. conversion of the amine inventory can be carried out at any time while the TGTU system is in full operation and does not require a shutdown.
In order to follow more stringent environmental regulations, some TGTU systems have incorporated a caustic wash unit downstream of the tail gas absorber. By doing so, the sulphur emission issue is in effect converted into a wastewater treatment task. Running a caustic wash unit is also an added cost and increases plant complexity. Application of an innovative, highly selective and high capacity solvent, such as OASE yellow, may allow the caustic wash unit to be mothballed.
Both case studies showcase the performance gain of existing TGTUs that have been converted to the new solvent. The same benefits also apply to new TGTUs. In addition, a grassroots design will be smaller in size, therefore resulting in lower capex.
Conclusion
OASE yellow solvent can reduce the operational cost and sulphur emissions of Claus TGTUs compared to plain MDEA or formulated (acidified) MDEA solutions. Alternatively, the capacity gain of OASE yellow can also be used to increase the SRU load and TGTU throughput.
Keeping the existing amine inventory of the tail gas unit means no disposal of material is necessary, which is both economic, and very environmental-friendly.






